Special Application Concrete
Micro-reinforced Concrete
Industrial concrete floors are structures that provide great mechanical and chemical resistance, primarily intended for increased daily traffic loads, heavy working machinery and/or resistance to various corrosive agents. By using micro-reinforced concrete with a special type of fibre, the investor is provided with significant financial savings in comparison to the use of conventional reinforcement. A special chemical additive as well as fibres are used to entrap a minimal amount of air into the concrete, while other compounds are specially designed so to achieve as little concrete shrinkage as possible. This is exactly the type of mix design that allows the increase of dilatation fields from standard 25-30 m2 to as much as 500 m2. The project does not require any preparatory work regarding the setting up of conventional reinforcement bars, and an additional saving of finance and time is achieved because it is not necessary to cut or fill the dilatations. Holcim has extensive knowledge and experience in concrete production, and such innovative approach delivers exceptional quality with significant financial savings.

Foam Concrete
Foam concrete is a type of lightweight concrete that is produced by adding foam to the fresh concrete mix design using a special foam generator. In this way, the air is drawn into the concrete, which ultimately reduces the density of the concrete. Foam concrete is easy to install, it is of good workability and pumpability, and has good insulating properties. It has a wide range of applications, in the reconstruction of road trenches, filling the cavities in hard-to-reach areas, filling unused containers, in the screed or floor glaze production etc.
Installation of foam concrete is not recommended in structures where significant structural shifts are expected.
Concrete for Special Environment Exposure Conditions
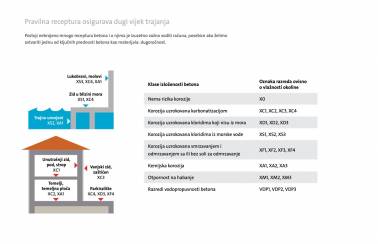
A proper receipt ensures a long life span, so Holcim Croatia pays special attention to the development of appropriate mix designs for concrete exposed to aggressive environmental conditions. The required exposure classes are obtained by analysing water and soil in contact with the hardened concrete in exploitation, and are then prescribed within the project. Namely, it is necessary to adjust the mix design, prescribe the maximum water-cement ratio and the minimum compressive strength class.
Some examples of the use of special concrete for projects in aggressive environments are the following:
- An environment is considered to be chemically aggressive when there is risk of non-sea chlorides (XD exposure class) and chemical corrosion caused by sulphates (XA exposure class), e.g. when building a wastewater treatment plant. For XA2 and XA3 exposure classes, the use of sulphate-resistant cement, i.e. concrete with sulphate resistance, is prescribed.
- When working in a marine environment, the danger to the structure arises from seawater chloride. The maximum water-cement ratio and the minimum amount of cement are prescribed. It is necessary to obtain a dense paste structure in order to keep the permeability of concrete as low as possible. XS3 is the most demanding class; it is used for structures in tidal zones where, in addition to chlorides, alternating humidity with the mechanical action of the waves is also in effect.
- Concrete structures exposed to the effects of freezing and thawing need to be durable to have an adequate resistance to this action and in cases such as road construction, to freezing and thawing in the presence of de-icing agents (exposure classes XF, XD, sometimes XM).
- The construction of hydrotechnical facilities, especially dams and hydroelectric power plants, requires a large volume of concrete, which causes the risk of cracks, so concrete and cement with low heat of hydration are needed (exposure classes XF1 and XF3, WP water permeability).
- When building animal breeding facilities, it is sometimes necessary to use sulphate-resistant cement due to risk of chemical corrosion, as faeces may contain a significant amount of sulphate (exposure classes XC, XA, sometimes XM, WP water permeability).
Self-compacting Concrete
Self-compacting concrete (SCC) is a special type of concrete with innovative features. Concrete fluidity and good resistance to the segregation of components when flowing ensures that the final product has a very homogeneous structure, minimum number of cavities, uniform compressive strength, and high-quality surface finish, which leads to increased durability of structures. The use of self-compacting concrete allows for greater efficiency and shorter installation time.
Hydromedia™
Hydromedia™, a sustainable solution of LafargeHolcim, is a unique and innovative system for managing rainwater. As urban population density increases, natural and green areas are progressively replaced by impermeable surfaces. The Hydromedia™ system enables good rainwater infiltration and provides an economical method for storing rainwater, i.e. it provides a solution that combines concrete properties and an advanced drainage technique.
The Hydromedia™ system consists of permeable concrete and a drainage base layer specially dimensioned depending on the specific characteristics of the location where it is installed. It contains approximately 20-35 of voids and allows water flow of 200 to 1.400 litres per square metre per minute. Rainwater drainage is possible directly into the drainage layer, and then into the surrounding terrain (replenishment of groundwater levels), or into drainage pipes through which it is drained into the public rainwater stormwater drainage system.
An additional advantage of this product is the bright colour of the concrete carriageway, which therefore absorbs and stores less heat from the sun.
The implementation of pervious concrete surfaces encourages the use of sustainable drainage systems (SuDS).
More about Hydromedia™ concrete

Roller-compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete is a special type of concrete which, except for the composition of the mixture and properties, differs from ordinary concrete in the way it is installed in the carriageway structure. Roller-compacted concrete is installed by compaction and rolling, instead of vibrating. It is used in the construction of promenades and pedestrian zones, bicycle paths, parking lots, carriageways for light and heavy traffic loads, traffic areas at gas stations, terminals and airport areas, traffic areas in tunnels, and can be used on highways if the upper surface is further processed. Roller-compacted concrete carriageways are built for longer design periods, with low maintenance costs during the entire life span and service life. Roller-compacted concrete has many advantages, such as improved visibility, reduced heat island effect, it is a heat resistant material, it has high resistance to wear, sliding, freezing, resistance to frost and salt, the use of various pigments is possible, and in addition to all that, roller-compacted concrete is an environmentally friendly material, since recycling is also possible.
More about roller-compacted concrete roads